ABS
Acrylonitril-butadieen-styreen (ABS)
ABS Plastic Injection Molding: Complete Guide to Process, Properties & Applications
What Is ABS Plastic?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a durable thermoplastic polymer used extensively in precision molding. Known for its high impact strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability, ABS is commonly applied in high-volume manufacturing across a wide range of industries.
Material Composition
ABS is a copolymer made of:
- Acrylonitrile – adds strength and chemical resistance
- Butadiene – enhances toughness and impact resistance
- Styrene – provides rigidity and a smooth surface finish
This combination results in a versatile material that softens when heated and hardens upon cooling, making it ideal for injection molding.
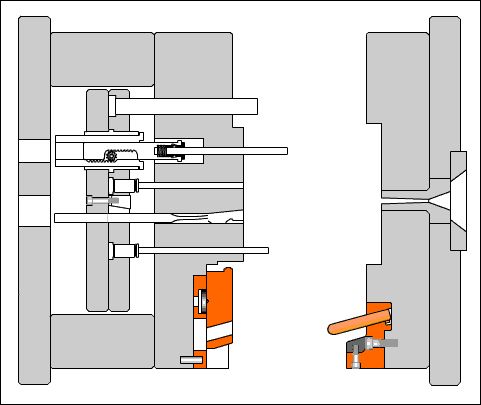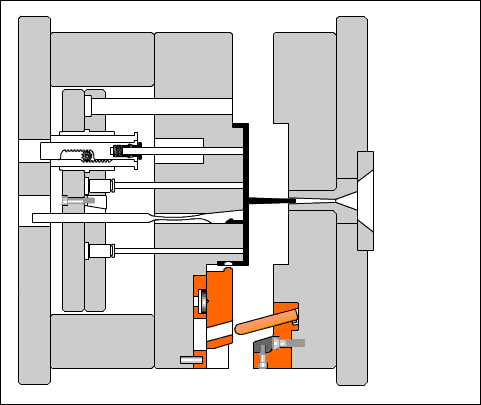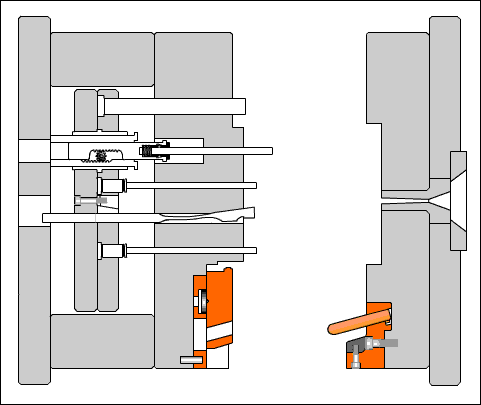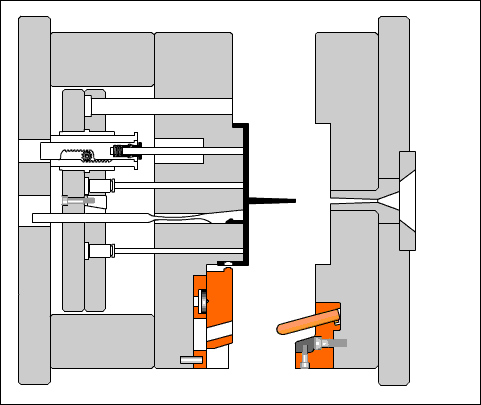
Understanding the ABS Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is a manufacturing process where molten plastic is forced into a shaped mold cavity. With ABS, this method enables the production of complex, highly accurate parts with consistent repeatability.
Step-by-Step Overview
- Material Drying
ABS pellets must be dried at ~80°C to prevent moisture-related defects like bubbles or streaking. - Melting Phase
The pellets are fed into a heated barrel where they are melted into a homogeneous molten mass. - Injection
The molten ABS is injected into a precision mold under high pressure to fill the cavity completely. - Cooling and Solidification
Once inside the mold, the material is cooled and solidified to take its final form. - Ejection
After cooling, the mold opens and the finished part is ejected automatically or with ejector pins.
Key Advantages of ABS Injection Molding
- Impact Resistance
Ideal for applications requiring strength and toughness. - Dimensional Accuracy
Maintains tight tolerances across various environmental conditions. - Aesthetic Surface Finish
Produces smooth, high-gloss parts that can be easily painted or coated. - Cost-Effective Production
ABS is more affordable than many other engineering-grade plastics. - Recyclability
As a thermoplastic, ABS can be reprocessed and reused, supporting sustainable manufacturing.
Limitations to Consider
Despite its many benefits, ABS does have some limitations:
- UV Sensitivity
Without stabilizers, ABS may discolor or degrade under prolonged sunlight exposure. - Flammability
Raw ABS is combustible and may require flame retardants for safety compliance. - Heat Resistance
ABS softens at relatively low temperatures (~105°C), limiting its use in high-heat environments.
Common Applications for ABS Molded Components
ABS is widely used in industries that require durable, lightweight, and attractive plastic parts:
Automotive
Interior panels, dashboards, trim parts, and structural brackets.
Electronics
Device housings, remote controls, computer components, and enclosures.
Consumer Products
Toys (e.g., building bricks), appliances, tool casings, and bathroom accessories.
Medical
Non-critical casings, handles, and custom enclosures.
Construction
Fittings, protective housings, wall panels, and more.
Best Practices for ABS Molding Success
- Use appropriate mold temperatures (60–80°C) to balance cycle time and surface finish.
- Incorporate proper draft angles to ease part release and avoid damage.
- Design gates and runners to ensure smooth material flow and minimal stress.
- Monitor moisture content to avoid quality defects like voids and silver streaks.
Why Choose ABS for Your Next Project?
Whether you're creating functional prototypes or scaling to mass production, ABS offers a powerful combination of strength, versatility, and affordability. Its adaptability makes it one of the top choices for high-precision injection molding across industries.
Start Your ABS Molding Project Today
Looking to develop high-quality ABS plastic components? We offer end-to-end support—from product design and tooling to injection molding and final assembly. Get in touch to learn how we can support your next manufacturing challenge.